Your organization’s goal should be to strive for the capability to:
1. prevent,
2. detect,
3. and respond
to cyberattacks targeting your data center.
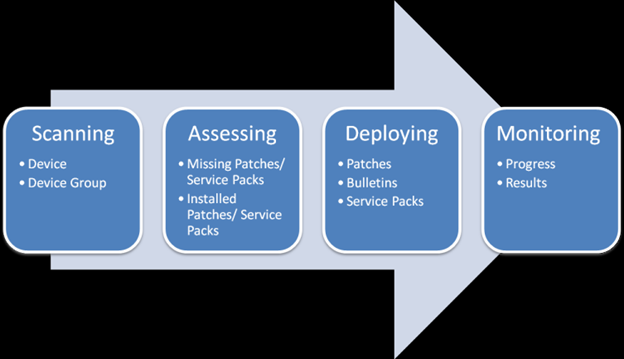
Your organization’s goal should be to strive for the capability to:
1. prevent,
2. detect,
3. and respond
to cyberattacks targeting your data center.
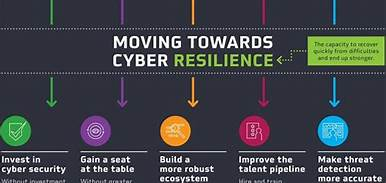
Cyber resilience is an evolving perspective that is rapidly gaining recognition. The concept essentially brings the areas of information security, business continuity, and organizational resilience together.
Organisations should establish a measurable cyber security program. The program translates the Cyber Security strategy into action, driving initiatives and continuous improvements in cyber resilience. The steering committee oversees the cyber security program.
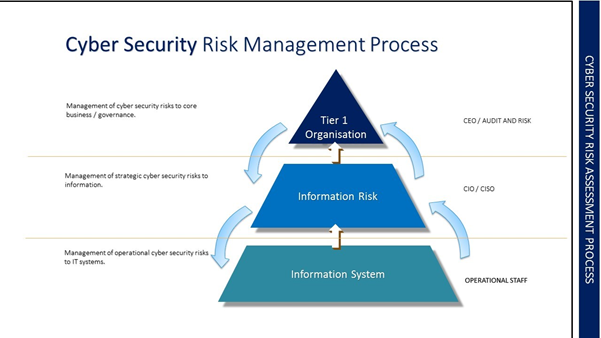
Translating a cyber security strategy and vision into action requires the buy-in and support of the wider organisation. This can be achieved by establishing a committee containing key stakeholders from across the business. The main objective of the steering committee is to achieve consensus and align cyber security priorities with the organisation’s objectives. Steering committees are most effective when they contain representatives who can make decisions on resource allocation, prioritisation, and direct cyber security activities.

Effective risk management is a core component of governance and must be embedded within the organisation. A framework is needed to effectively identify, analyse, evaluate, and manage cyber security risks. The framework supports consistent decision-making and prioritisation within an organisation, maximising the benefit of investment in cyber security.

Achieving effective cyber security governance requires defining and establishing the organisation’s cyber security roles and responsibilities. After they are created, consider at what level in the organisation they need to be performed.
In smaller organisations, most cyber security functions may fall to a single person. In such cases, it is even more important for senior leaders to ensure cyber security duties are realistic, clearly understood, and well communicated. Everyone in the organisation should understand their role in supporting effective cyber security.
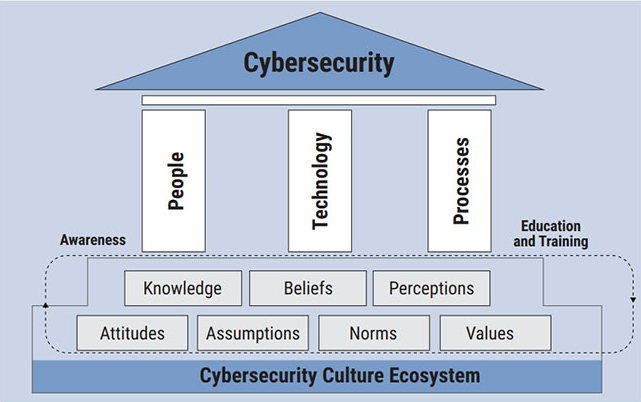
An effective cybersecurity culture enables a virtuous circle where employees, understand their roles and responsibilities for protecting their firm, literally becoming human firewalls.
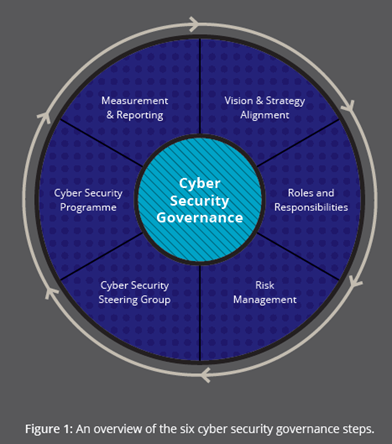
Every organisation’s journey toward cyber resilience will be different. Navigating the individual complexities of governance requires leaders to chart their organisation’s own course. The terms cyber resilience and cyber security are both used in Charting Your Course. Cyber resilience is suggested as a realistic goal for an organisation; rather than focusing primarily on prevention of cyber incidents, resilience also emphasises the importance of recovery and response.
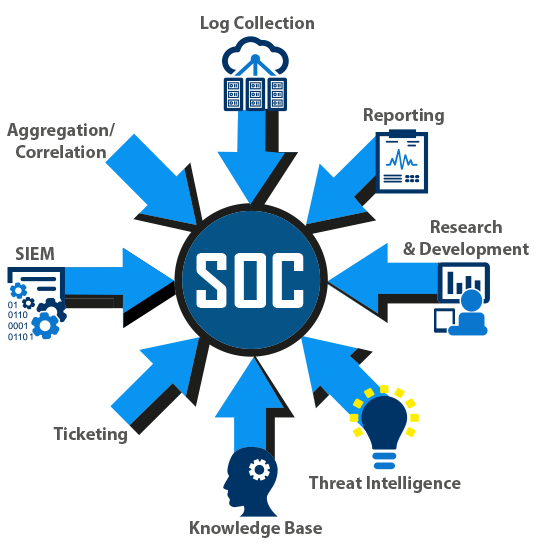
Bad actors do not rest and neither does the Tri-Paragon’s AGILEBLUE SOC-as-a-Service.
Our SOC platform is based on proactive prevention techniques that are built on machine learning, so they are adaptive, constantly improving, and always ready to identify the latest threat.

Tri-Paragon Inc. 130 King Street West, Suite 1800, P.O. Box 427, Toronto, ON Canada M5X 1E3
Phone: 416.865.3392 Email: info@triparagon.com
(The science of performance)
“If you think it is expensive to hire a professional to do the job, wait until you hire an amateur” Red Adair
Disaster Recovery Plan Consists of 2 primary inputs- Business Impact Assessment and Risk Analysis
Business Impact Analysis and Risk Assessment are both important components of BC/DR Plans. However, Business Impact Analysis should be carried out before attempting Risk Assessment. Once both these components are in place, it is easier to formulate a sound strategy and plan for Business Continuity / Disaster Recovery.
The four most important risk scenarios that affect business operations of an organization are:
1. Production site is partly or fully destroyed or cannot be accessed
2. Loss of data and / or other critical records
3. Loss of IT functions due to application software errors, glitches, viruses, power outages etc.
4. Loss of skills due to incapacitation, pandemics, death or mission-critical staff leaving for greener pastures