Menu
- 130 King Street West, Suite 1800
- P.O. Box 427
- Toronto, ON, Canada M5X 1E3
- (416) 865-3392
- info@triparagon.com
Webopedia defines hyperconvergence as follows: “Hyper-convergence (or hyperconvergence) is a type of infrastructure system that is largely software-defined with tightly-integrated compute, storage, networking and virtualization resources. This stands in contrast to a traditional converged infrastructure, where each of these resources is typically handled by a discrete component that serves a singular purpose. Hyper-convergence is also called hyper-converged infrastructure.

IDC Analyst Definition of Hyperconverged Infrastructure: A solution that natively collapse core storage, compute, and storage networking functions into a single software solution or appliance. In addition all hyperconverged systems employ:
Why Do Data Center Consolidation?
How Does Hyperconverged Infrastructure Impact the Data Center?
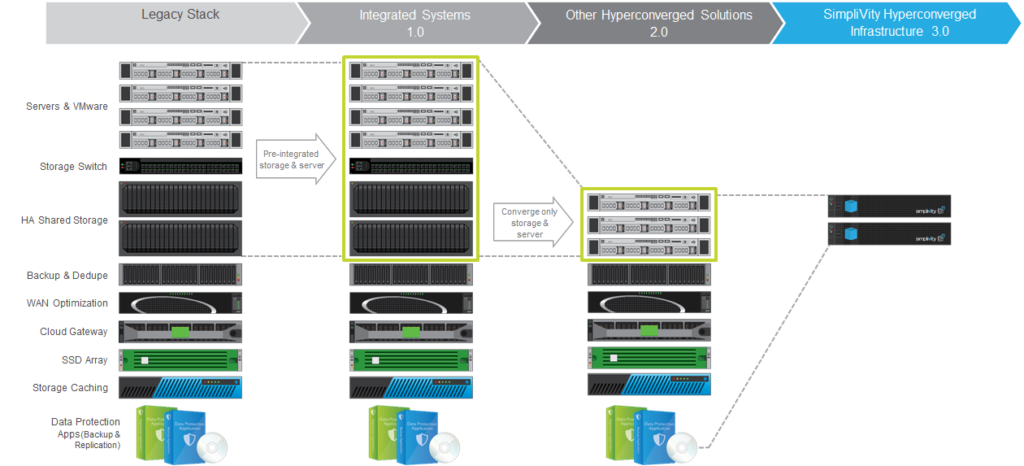
The Evolution of Hyperconverged Systems
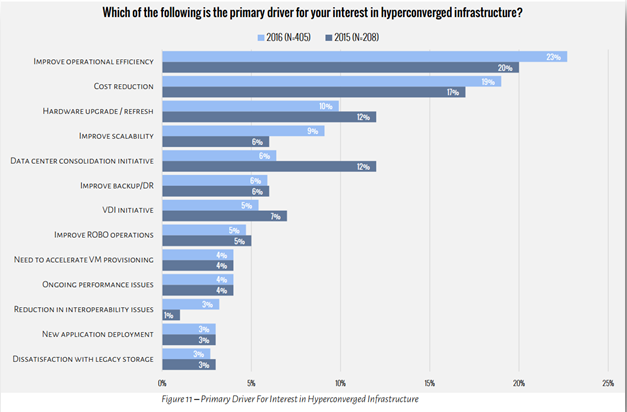
Why Adopt a Hyperconverged Infrastructure
Source: 2016 State of Hyperconverged Infrastructure Market; ActualTech Media.
What to Look for In a Hyperconverged System.